ELECTRIC ARC FURNACE
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc.
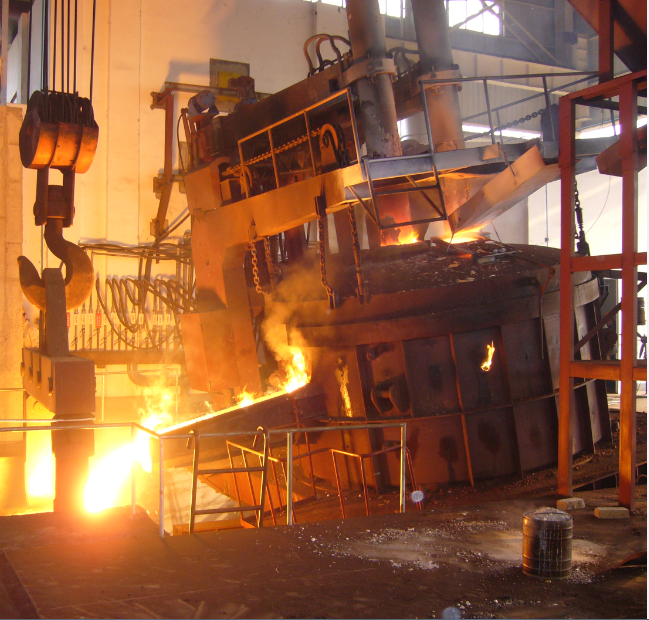
Industrial arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one-tonne capacity (used in foundries for producing cast iron products) up to about 400 tonne units used for secondary steelmaking. Industrial electric arc furnace temperatures can reach 1,800 °C (3,300 °F), while laboratory units can exceed 3,000 °C (5,400 °F).
In electric arc furnaces, the charged material (the material entered into the furnace for heating, not to be confused with an electric charge) is directly exposed to an electric arc, and the current from the furnace terminals passes through the charged material. Arc furnaces differ from induction furnaces, in which the charge is heated instead by eddy currents.
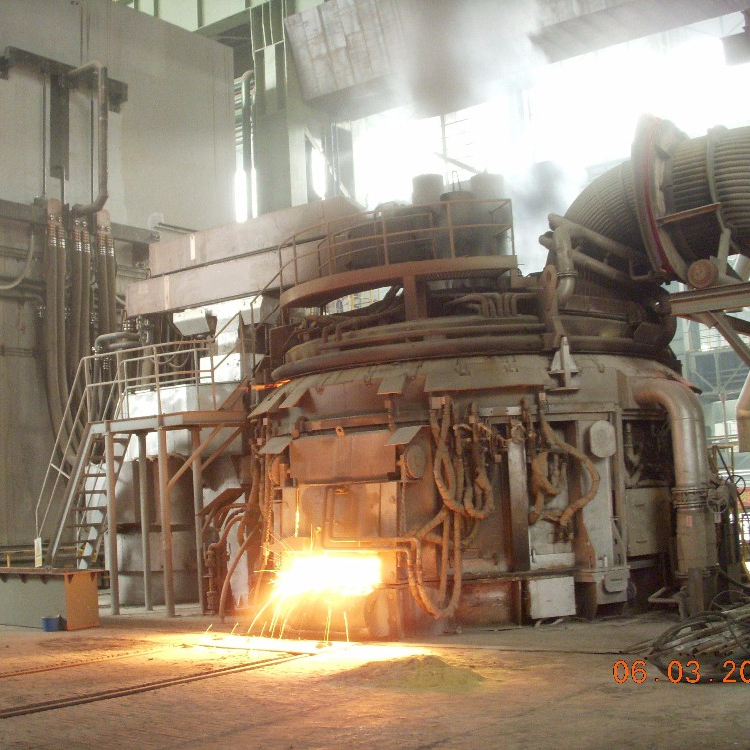
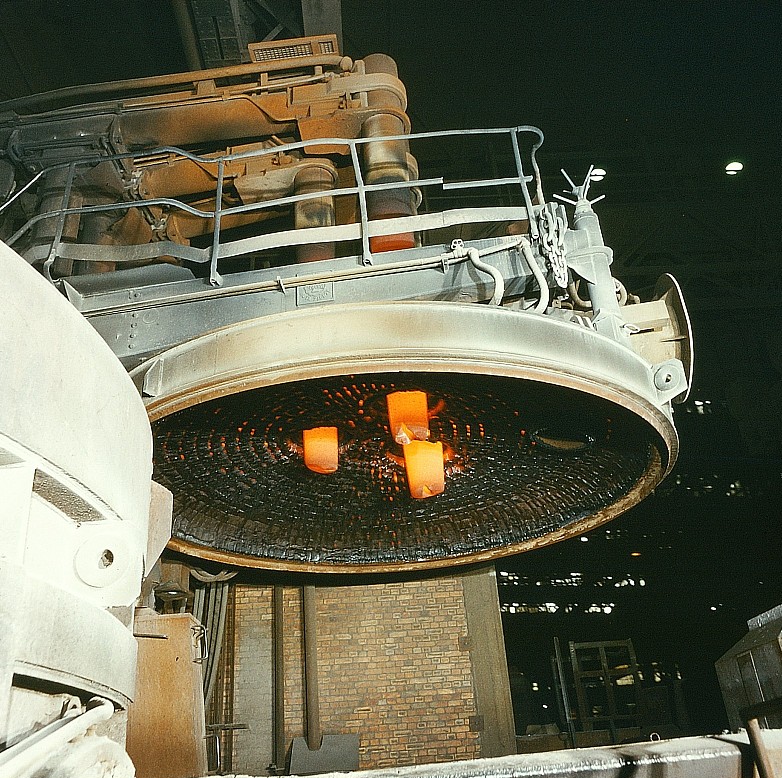
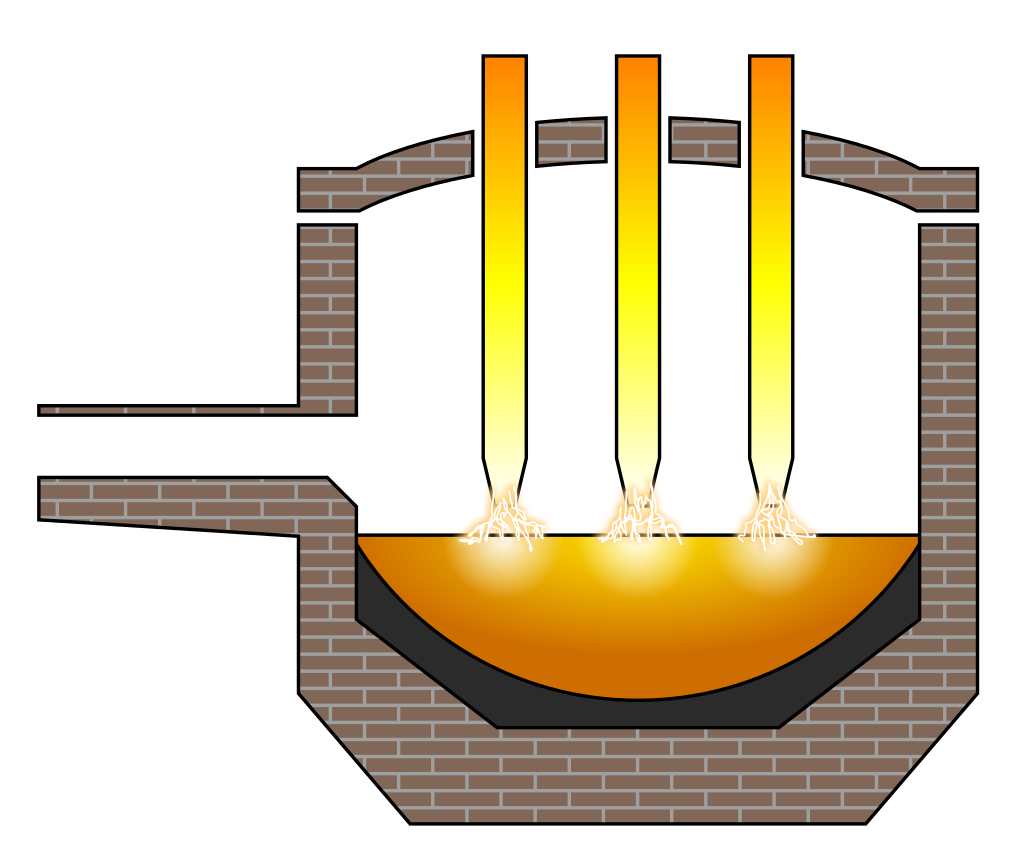
An electric arc furnace used for steelmaking consists of a refractory-lined vessel, usually water-cooled in larger sizes, covered with a retractable roof, and through which one or more graphite electrodes enter the furnace.[5] The furnace is primarily split into three sections:
- the shell, which consists of the sidewalls and lower steel “bowl”;
- the hearth, which consists of the refractory that lines the lower bowl;
- the roof, which may be refractory-lined or water-cooled, and can be shaped as a section of a sphere, or as a frustum(conical section). The roof also supports the refractory delta in its center, through which one or more graphite electrodes enter.
Megatherm Electric Arc Furnace Product Range:
5 Ton EAF to 50 Ton EAF
Most Recent Commissioning:
Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) 2021
Advantages of Megatherm Arc Furnace
- Megatherm’s 30 year old and industry-leading design team
- Use of future-proof technologies and design
- Megatherm’s vast service network
- Lightning fast service and troubleshooting
- Exhaustive PLC-based auto diagnostics, preventive alarms and maintenance notifications
- Remote access for off-site troubleshooting and servicing